Ageing brings natural physical changes and increased susceptibility to certain health conditions. Being vigilant and proactive allows early detection and prevention of common age-related issues. Here are key health concerns that gain importance as we get older.
Health Concerns in Aging: What to Monitor for Optimal Well-being
1. Heart Disease

Heart disease risk rises with age. Contributing factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure and inactivity also become more prevalent in later decades.
Get regular cardiac check-ups. Know warning signs like chest pain, dizziness and shortness of breath and seek prompt treatment if they occur. Improve diet, exercise, and sleep habits to protect your heart over the long term.
2. Diabetes
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as we age, particularly beyond 40. Insulin resistance can creep up through the combined effects of lifestyle factors and biological changes. Get bloodwork done annually to monitor for elevated glucose.
Reduce your diabetes risk through healthy eating with less sugar and refined carbs, achieving a healthier weight, and staying active. If diagnosed, work closely with your doctor to optimally manage blood sugar levels.
3. High Blood Pressure
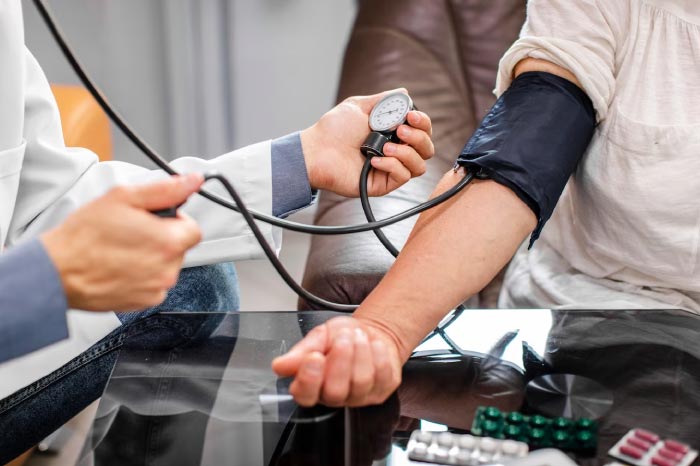
Blood pressure tends to increase with age, raising risks of stroke, heart disease and kidney damage if left untreated. Have your blood pressure measured at least annually and more frequently if borderline or high readings are detected.
Adopting a low-salt diet, maintaining a healthy weight through exercise, limiting alcohol, and medications can help control hypertension.
4. Cancer
Cancer risk increases significantly as we age. Ensure you stay up to date on recommended cancer screenings like mammograms, colonoscopies, prostate exams, skin checks and Pap tests.
Also, know the warning signs of common cancers to seek prompt evaluation of unusual symptoms. Leading a healthy lifestyle helps lower overall cancer risk.
5. Arthritis

The wear and tear of ageing frequently manifests as osteoarthritis – stiff, painful joints from loss of cushioning cartilage. Weight management, low-impact exercise, physical therapy, assistive devices, and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage arthritis.
Some dietary supplements may provide modest relief too. Joint replacements can transform the quality of life when damage is severe.
6. Urinary Incontinence
Loss of bladder control becomes more common with age. Urinary incontinence has numerous causes including UTIs, constipation, prostate issues, vaginal atrophy, and pelvic floor weakness.
See a doctor to identify the source, then adopt lifestyle changes like weight loss and Kegel exercises. Many effective treatment options are available for managing incontinence.
7. Hearing Loss

Gradual hearing decline due to inner ear nerve and sound perception cell damage is common with ageing. Be aware of not fully hearing conversations, needing to raise television volume, or having difficulties hearing higher-pitched sounds.
See an audiologist for hearing tests every few years after age 50. Hearing aids can improve quality of life considerably if issues emerge.
8. Respiratory Diseases
Lung capacity and immune function decrease with age, increasing susceptibility to respiratory diseases like pneumonia, COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer.
Know warning signs of respiratory illness and seek prompt diagnosis. Smoking cessation, vaccines, activity, and lung-healthy nutrition provide key prevention.
9. Neurocognitive Decline

Subtle memory lapses and slower thinking become more noticeable in senior years, though not necessarily indicative of dementia. However, cognitive decline does increase the risks of full-blown dementia.
Keep your mind sharp through regular exercise, learning new skills, social interaction, and brain-training activities. Also treat hearing loss, depression, and other factors potentially influencing cognition.
10. Skin Changes
Our skin becomes thinner, drier, and less elastic over time. This leads to wrinkles, age spots, bruising and injuries more easily. Moisturise daily and use sun protection to prevent further sun damage.
Also, get familiar with your normal skin markings so any abnormal changes like new moles can be evaluated promptly by a dermatologist to catch potential skin cancers early. It’s always much better to go and find out whether it’s something that you need to worry about instead of ignoring it.
11. Hair Loss
Hair gradually thins and greys as we get older, due to decreased production and follicle shrinkage over time. While ageing hair changes cannot be prevented outright, ensure you maintain adequate protein, iron, and vitamins like biotin to support healthy locks. Gentle hair care also helps reduce the breakage of fragile strands.
If hair loss becomes significant, there are hair loss treatments available. You can find a treatment for hair loss at an online pharmacy if you don’t feel comfortable talking to someone about it in person.
Look for an online pharmacy that can explain the different options available and find the best hair loss treatment plan for you.
12. Weight Gain
Metabolism naturally slows with age, making weight gain easy if eating and activity habits don’t adjust. Work to be vigilant about portions, reduce empty calories, choose nutritious whole foods, and keep moving regularly as you get older.
Even moderate exercise helps counteract age-related weight creep. Don’t dismiss a few extra pounds – maintaining a healthy weight reduces risks of diabetes, hypertension, osteoarthritis, heart disease and cancer.
13. Insomnia

Insomnia becomes more prevalent in later decades, stemming from age-related changes in sleep architecture and circadian rhythms. Develop consistent sleep habits and wind-down routines to promote sufficient, restful sleep.
Limit screen time before bed. Review medications with your doctor as some may disrupt sleep. Overall good health habits also improve sleep quality.
14. Oral Health Decline
Our teeth and gums become more vulnerable to decay and infection as we age. Brush thoroughly twice a day and see your dentist frequently to catch issues early. Report mouth pain, loose teeth, chewing issues or mouth sores promptly.
Support oral health through diet, hydration, tobacco avoidance and regular dental cleanings and x-rays.
15. Depression

The increased social isolation, medical challenges and loss often accompanying ageing can trigger depression and anxiety in older adults. It’s also easier to ignore those feelings when you’ve got a lot of other responsibilities like a challenging job or a family to look after.
Report persistent low mood, loss of enjoyment, changes in sleep and appetite to your doctor for assessment rather than dismissing symptoms as just part of getting older. Counselling, medications, and lifestyle changes help manage geriatric mental health issues.
16. Infections
An ageing immune system makes older adults more prone to infections like pneumonia, UTIs and skin infections. Maintain protection through vaccination, safe food handling, avoiding unwell people, and practising good hygiene.
Report signs of infection like fever and chills promptly for diagnosis and treatment. Preventing infections from turning serious is key.
17. Chronic Inflammation

Inflammation increases with ageing due to accumulated cell damage and poorer immune regulation. Chronic inflammation contributes to many age-related diseases.
Following an anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, fruits, vegetables, and fibre tames unnecessary inflammation. Staying active also lowers inflammation levels.
18. Anaemia
Anaemia, a deficiency of healthy red blood cells, increases with age due to gastrointestinal issues that impede iron absorption plus other complications. Symptoms like weakness, fatigue and rapid heartbeat should prompt medical review.
Your doctor can advise appropriate dietary changes or supplements to optimise red blood cell health.
Final Thoughts
Ageing brings natural physical changes and vulnerability to certain conditions, but many age-related health issues can be delayed or managed through healthy lifestyle measures and proactive medical care.
Pay attention to your body, get recommended health screenings, and report worrying symptoms promptly. Prioritising prevention and early intervention helps maintain comfort, independence, and vitality in your later years.





